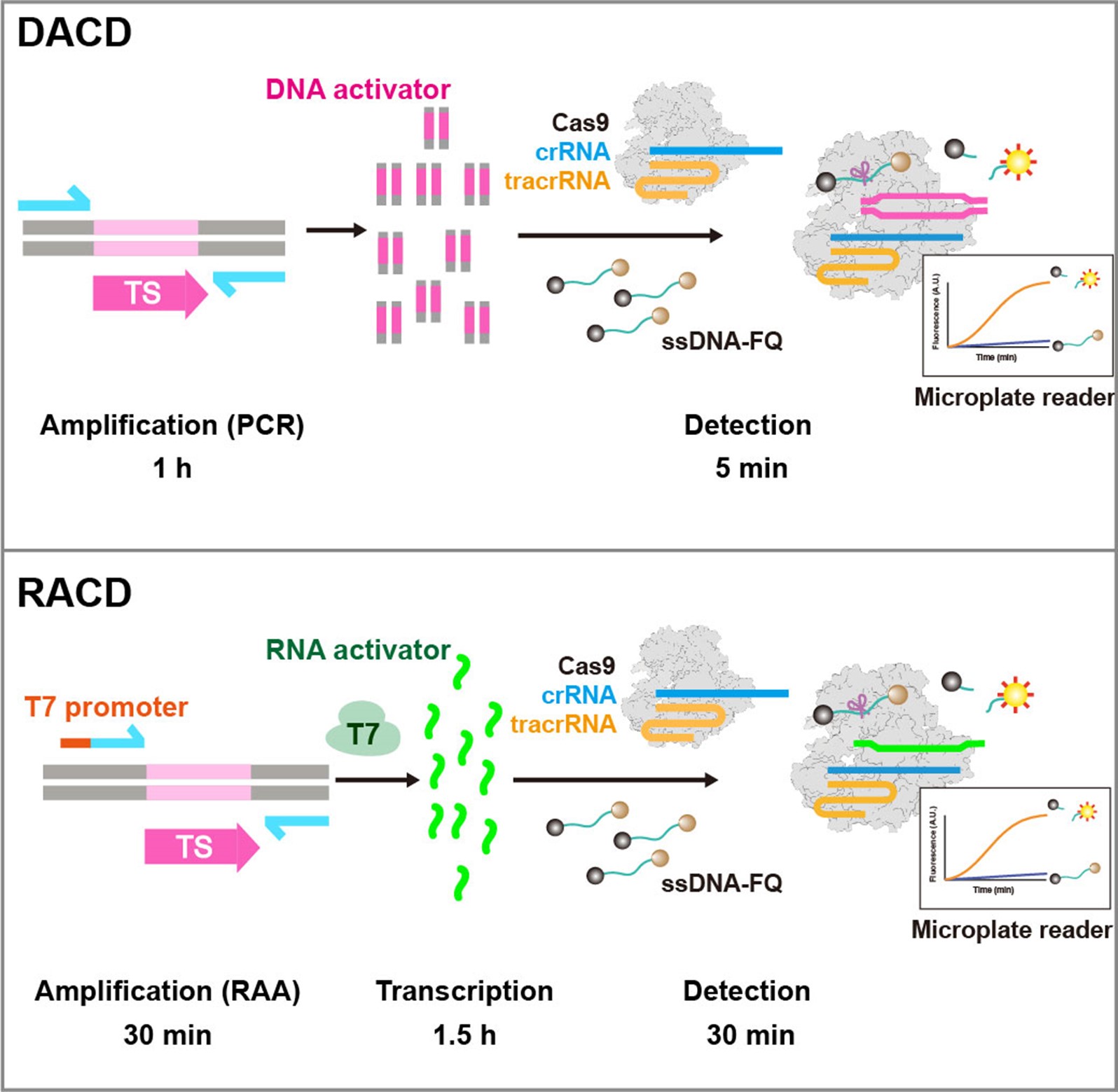
Abstract: Type V and type VI CRISPR–Cas systems have been shown to cleave nonspecific single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) in trans, but this has not been observed in type II CRISPR–Cas systems using single guide RNA. We show here that the type II CRISPR–Cas9 systems directed by CRISPR RNA and trans-activating CRISPR RNA dual RNAs show RuvC domain-dependent trans-cleavage activity for both ssDNA and ssRNA substrates. Cas9 possesses sequence preferences for trans-cleavage substrates, preferring to cleave T- or C-rich ssDNA substrates. We find that the trans-cleavage activity of Cas9 can be activated by target ssDNA, double-stranded DNA and ssRNA. The crystal structure of Cas9 in complex with guide RNA and target RNA provides a structural basis for the binding of target RNA to activate Cas9. Based on the trans-cleavage activity of Cas9 and nucleic acid amplification technology, we develop the nucleic acid detection platforms DNA-activated Cas9 detection and RNA-activated Cas9 detection, which are capable of detecting DNA and RNA samples with high sensitivity and specificity.
Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-024-02255-7