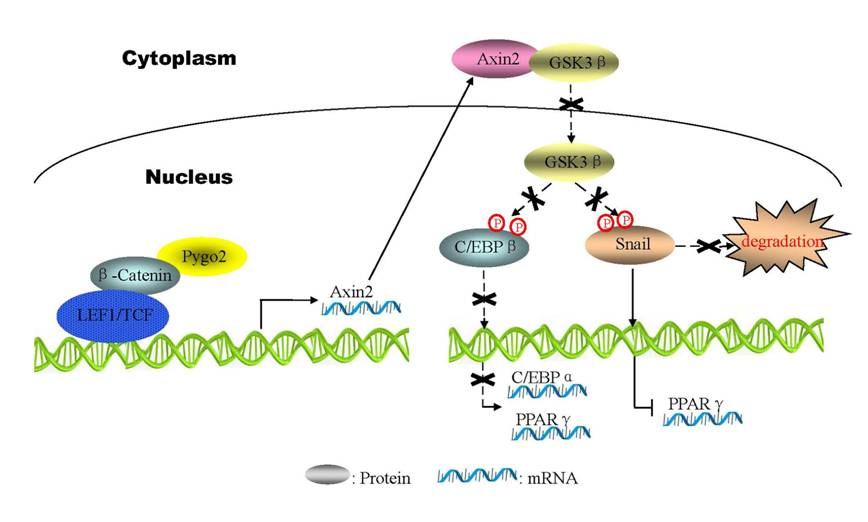
Abstract: Wnt/β-Catenin signaling plays a key role in regulating adipogenesis through indirectly inhibiting the expression of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ); however, the detailed molecular mechanism remains poorly understood. Moreover, the factor(s) that determines the Wnt/β-Catenin output level during adipogenesis is also not completely defined. In this study, we showed that Pygo2 exhibited a declined expression pattern during adipocyte differentiation, resulting in an attenuated Wnt/β-Catenin output level. Mechanism study indicated that Pygo2 inhibition led to the downregulation of Axin2, a constitutive Wnt target, in the cytoplasm. Consequently, Axin2-bound GSK3β was released and translocated into the nucleus to phosphorylate C/EBPβ and Snail, resulting in an increase in the DNA binding activity of C/EBPβ and decreased protein stability of Snail, which subsequently activated the expression of C/EBPα and PPARγ. Consistent with this, embryonic fibroblasts from Pygo2 -/- mice exhibited spontaneous adipocyte differentiation, and adipocyte precursor-specific Pygo2 deficient mice exhibited increased adiposity with decreased energy expenditure. We further showed impaired glucose tolerance and decreased systemic insulin sensitivity in Pygo2 deficient mice. Our study revealed an association between Pygo2 function and obesity or diabetes.
Link: http://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/early/2018/09/27/db18-0311.long